(Source: Microsoft)
Revolutionary Australian Chip Among Major Advances in Quantum Computing
A team of Australian and Microsoft researchers reinvented a cryogenic chip that will mean a new generation of “high performance” quantum computers that can operate faster and better, according to a story in technewsworld.com. Other news in the quantum realm includes IBM’s new quantum open-source software that is expected to operate a hundred times faster in two years—and Microsoft’s announcement that its Azure Quantum computer cloud service is open to the public.
Aussie Breakthrough
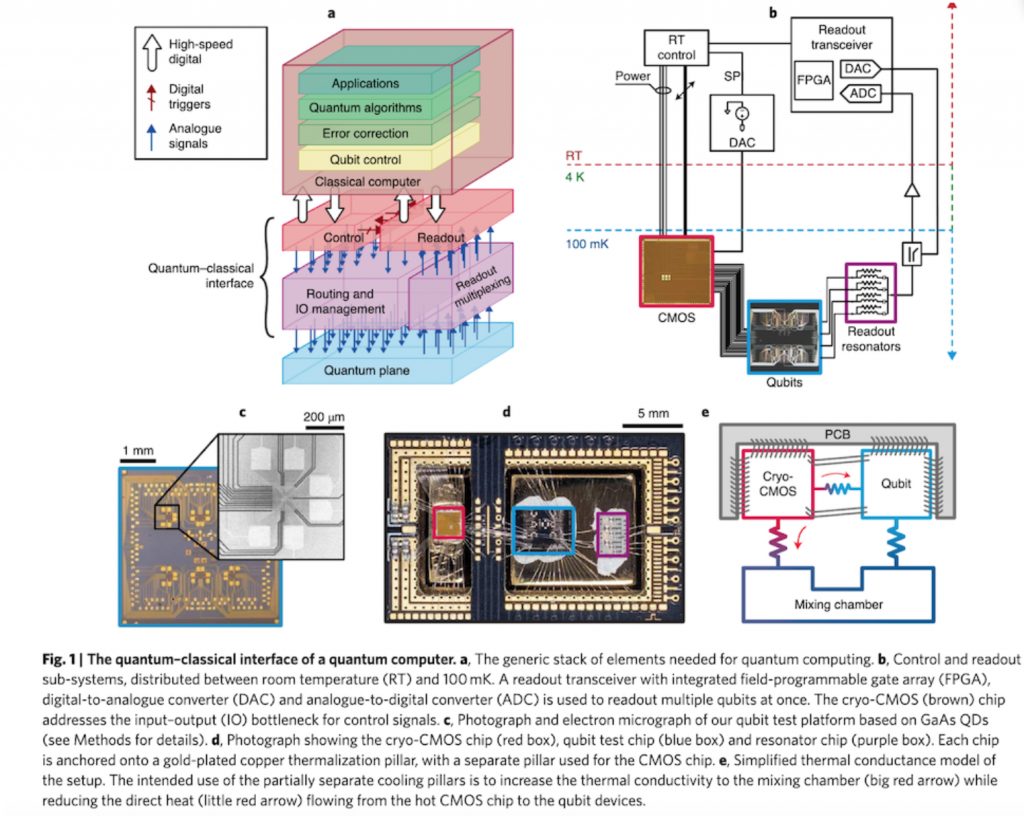
The “Gooseberry Chip” will revolutionize quantum computers because they were limited in the past to no more than 50 qubits because of architectural problems related to the cold temperatures required for operating the computers. With chips that can be kept at absolute zero, an unlimited number of qubits can be used.
A team of scientists and engineers at the University of Sydney, Microsoft and EQUS the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Engineered Quantum Systems developed the chip. Their findings were published in the Jan. 25 issue of Nature Electronics.
Because most quantum systems require qubits to operate at temperatures close to absolute zero (-273.15 degrees Celsius), the chip is a game-changer, since temperature and architecture can influence qubits.
Heather West, a senior research analyst at IDC, said the cold temperatures will help eliminate errors.
“The more qubits you have,” West said, “the better performance your computer will have. The problem is that when qubits begin working with one another—a process called entanglement—because they’re so unstable, they can begin working incorrectly, or decoherently. As you scale up, decoherence increases.”
She added that there’s another advantage to working at close to absolute zero. “To achieve super cold temperatures, you need to work in a vacuum, which helps reduce the environmental effects on the qubits,” she said.
read more at technewsworld.com
IBM to Upgrade Quantum Software
IBM says it will release software applications that are expected to become 100 times better-performing over the next two years, according to a story on cnet.com. The software will be written primarily with open-source code that users can contribute to and benefit from, IBM said in a statement:
“IBM’s planned quantum computing software releases are part of an effort to hide away as much of the quantum computing complexity as possible for ordinary folks. Getting a quantum computer to do useful work today is pretty tough, even with specialists like Zapata Computing and Cambridge Quantum Computing to hold your hand.”
The increased speed means jobs that took months on a classical computer could be finished in a few hours.
read more at cnet.com
The Gooseberry chip and cryo-computing core are breakthroughs for a Microsoft team and Australian researchers. (Source: computing.co.uk)
Microsoft Opens Azure Quantum Cloud
Microsoft made its Azure Quantum service via the cloud available last week, including quantum computers made by Honeywell and IonQ, according to a cnet.com story. The computers use a design called an ion trap that uses electrically charged atoms as qubits to store and process information. Microsoft plans to add another design by Quantum Circuits, whose qubits are supercooled electrical circuits, in the future.
“The opening of Azure Quantum marks the latest step in the commercialization of quantum computing, which promises to tackle problems that are out of conventional machines’ reach. BMW, Airbus and Roche are among those trying out quantum computers, although it will be years before it’s practical for more than research projects.”
Microsoft will be using the “Gooseberry” chip to enhance its quantum computers, it announced.
read more at cnet.com







Leave A Comment