Chinese Officials Influence Global Security, Movies
A recent series in The New York Times delves into the complexities of Chinese industry and outlines the economic growth as being “10 times faster” than the United States over the past four decades, and still more than twice as fast in the past few years. Much of its past growth was centered around manufacturing, but technology is catching up as a driver of economic growth.
The series outlined a lot of the issues that are of concern for American countries, but which also impact Chinese companies, which are burdened by the overriding interests of their Communist government:
- China exercises censorship over internet companies, banning politically unpopular content, criticism of the government and “distasteful” content it deems too raunchy, flirty, creepy or weird.
- China demands an interest in the most profitable companies.
- China’s law enforcement uses some apps, such as SenseTime, to track what its citizens are doing or saying through facial recognition technology.
- China allows companies to exploit each other’s technologies and doesn’t enforce copyright laws or intellectual property rights.
Internet Advances
The internet offers great opportunity both as a generator of income within the country, but also as an innovator that influences worldwide technology development, according to one story in the series with the headline, “How China Walled Off the Internet.”
China has surpassed the United States in smartphone payment usage and has adopted short videos, podcasts blogs and streaming TV as creative outlets. The mobile companies TenCent and ByteDance keep users engaged on mobile devices with apps such as Tencent’s widely used WeChat app that enables talking, paying bills, playing games and booking travel, among other uses.
The internet companies are invading traditional industries, too, like finance, media and healthcare. Alibaba is another company, like TenCent, that has a widely used mobile payment platform that has given it a dominant market share.
 High Tech Manufacturing
High Tech Manufacturing
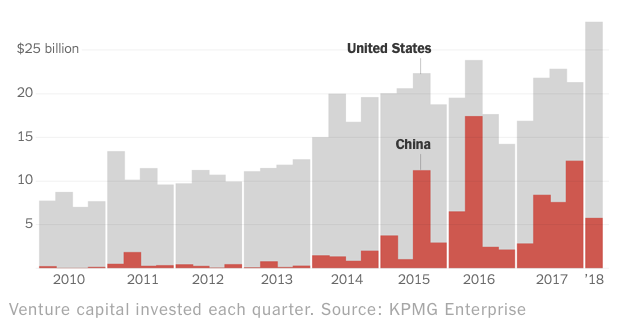
Another story called “How China Took Over Your TV” explains how the country went from being a place where American companies hired them to assemble parts manufactured elsewhere to a place where companies can make TVs, cell phones and other computers entirely from Chinese-made parts. Venture capital flowing into the country has helped fuel the growth, but also innovation and outside money from other countries, especially American-based tech companies that have satellite offices in China.
Film Industry Influence
The story “How China Is Rewriting Its Own Script” outlines the oversized influence the country wields in the movie industry because of its market share. The creators of “Pixels,” for instance, changed a scene in which aliens blow a hole in the Great Wall of China and made it the Taj Mahal instead to avoid problems with a release in China.
In a remake of Red Dawn, the MGM studio erased all references to an invasion by China in a small American town and changed film frame by frame to alter the villains into North Koreans, in deference to the country. Other older American films critical of Chinese policies, such as “Seven Years in Tibet,” are nowhere to be found in the country.
China has also influenced films by investing in them as producers. In the past five years, the country has contributed millions in funding in 41 top-grossing Hollywood films. For the first time, the Chinese market surpassed the U.S. movie market in sales during the first quarter of 2018.







Leave A Comment