Report: AI Medical Advances Possess Great Potential
The top three AI healthcare applications with the greatest financial potential include robotic surgery, virtual nursing assistants and administrative workflow automation, according to a report from Accenture, as reported in Venturebeat.com by Deena Zaidi. More than $150 billion could be save in healthcare costs from new AI tech, the report predicted.
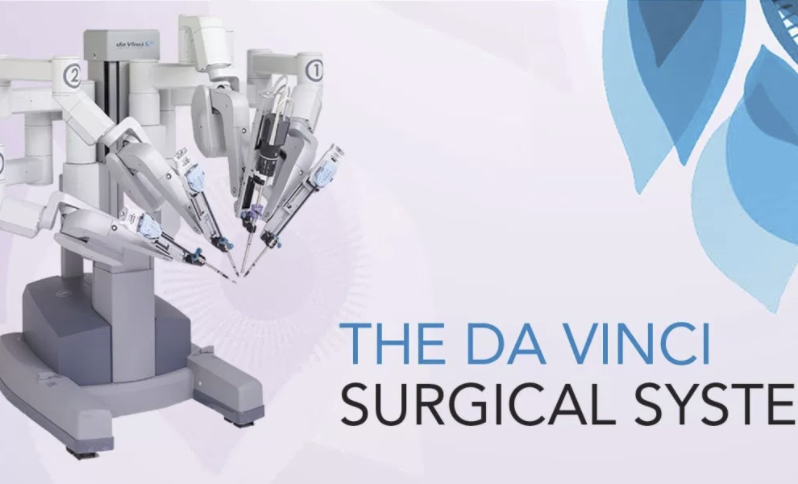
Robotic surgeries are considered “minimally invasive”—meaning the substitution of large incisions with a series of quarter-inch incisions and utilize miniaturized surgical instruments. AI surgical robotics combines data from real surgeries and records to improve surgical techniques. Better surgery leads to a 21 percent reduction in a patient’s length of hospital stay post-operation. The AI surgery robots da Vinci, a precise robotic surgery aid, and Heartlander, a miniature mobile robot that enters the chest to provide a.
Virtual nursing assistants could reduce unnecessary hospital visits and lessen the burden on medical professionals. According to Syneos Health Communications, 64 percent of patients reported they would be comfortable with AI virtual nurse assistants, listing the benefits of 24/7 access to answers and support, round-the-clock monitoring and the ability to get quick answers to questions about medications.
San Francisco-based virtual nurse assistant Sensely recently raised $8 million in Series B funding to put fleets of AI-powered nurse avatars to clinics and patients. The key goals of the technology are to keep patients and care providers in contact between office visits and to prevent hospital readmission. Sensely’s most commonly referenced nurse is Molly, which uses a proprietary classification engine and listens and responds to users.
Automation of administrative workflow ensures that care providers prioritize urgent matters and can also help doctors, nurses, and assistants save time on routine tasks. Some applications of AI on the administrative end of health care include voice-to-text transcriptions that automate non-patient care activities like writing chart notes, prescribing medications, and ordering tests.
An example of this comes from Nuance. The company provides AI-powered solutions that rely on machine learning to help health care providers cut documentation time and improve reporting quality. Computer-assisted physician documentation (CAPD) like this offers real-time clinical documentation guidance that helps providers ensure their patients receive an accurate clinical history and consistent recommendations.
And while these advancements are saving lives and helping promote good health, they also save a lot of money for healthcare systems bringing them on board their operations.
A recent report from Accenture analyzed the “near-term value” of AI applications in health care to determine how the potential impact of the technology stacks up against the upfront costs of implementation. Results from the report estimated that AI applications in health care could save up to $150 billion annually for the U.S. health care economy by 2026.
Reducing human error and improving patient outcomes are the hoped-for results of these three AI-driven technologies. The only drawback is a lack of human intervention and the possibility of computer errors. Also, data privacy remains one of the biggest challenges to AI-dependent health care.





Leave A Comment