UCLA Lab Extends Holograms with Deep Learning
Researchers at the University of California Los Angeles are applying deep learning to extending the depth of holograms, making it possible to create more accurate medical images, according to phys.org.
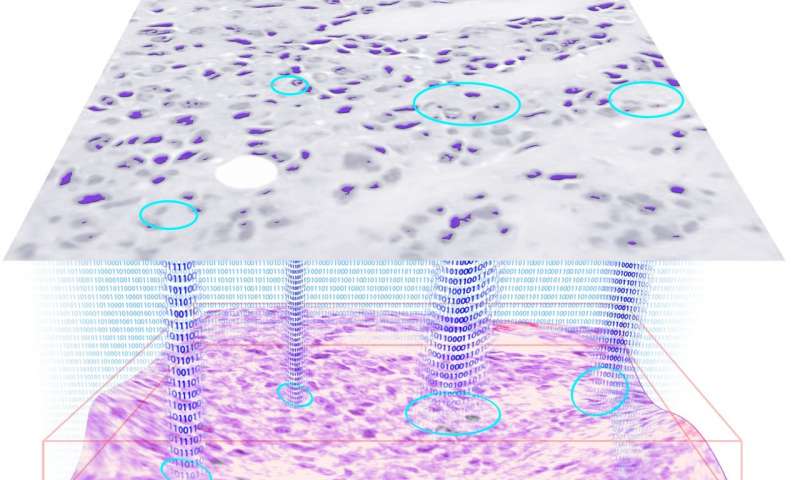
The image processing, which leverages multiple neural networks, could also automate identification and labeling of abnormal regions in medical scans, according to an in-depth story in Futurism.com. The story cites an article published in the journal Light: Science & Applications that showed how blood, Pap smears and other thin tissue samples could be examined in faster and greater detail.
“In holography, image reconstruction requires performing autofocusing and phase recovery, which are in general cumbersome and time-consuming to perform over a large sample volume,” according to the phys.org article. “In a recent article published in Optica, a journal of the Optical Society of America, UCLA researchers have demonstrated a new approach they termed HIDEF based on a convolutional neural network that simultaneously performs autofocusing and phase recovery to significantly extend the image depth of field and the reconstruction speed in holography.”
Dr. Aydogan Ozcan, the Chancellor’s Professor of electrical and computer engineering at UCLA, Yichen Wu, a graduate student and Dr. Yair Rivenson, a postdoctoral scholar, are heading the research.
read more at phys.org






Leave A Comment